class a foam acts as a surfactant which means that it
In this regime the bubble size depends largely on the orifice Reynolds number and a natural foam fractionation occurs causing higher surfactant concentrations at the top of the foam. This type of agent is very similar to Class A foam with regard to increasing wetting effectiveness of the water but does not have the foaming abilities.

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications
1 Type of foam concentrate used.

. Surfactants are any materials that interact with surfaces thus the term surfactant or surface. A surfactant when present in small amounts reduces surface tension of a liquid reduces the work needed to create the foam or increases its colloidal stability by inhibiting coalescence of bubbles. Therefore a surfactant contains both a water-insoluble component and a water-soluble component.
Water Foam Class A concentrate is simply a surfactant similar to dishwashing soap that reduces surface tension. These foams are not really considered in these apps. An example would be like cooling a glass of water with a single ice cube.
Surfactants are an extraordinary class of versatile amphiphilic compounds which have a spatially distinctive polar hydrophilic head and non-polar hydrophobic tail group. A foaming agent is a material that facilitates the formation of foam such as a surfactant or a blowing agent. Foams designed for flammable liquids.
Class A foam will increase wetting effectiveness which allows for greater penetration into Class A fuels. Class B foam is used on flammable liquids. Surfactants are usually organic compounds that are amphiphilic meaning they contain both hydrophobic groups their tail and hydrophilic groups their head.
Class A foam is biodegradable and non-toxic so it is environmentally sustainable. This corresponds to average volumetric rates of 45 and 9 Lhr. When added to water the resulting foam solution consists of many smaller droplets with much more surface area allowing faster heat absorption.
In addition the portion of the foam concentrate molecule that repels other water in order to break the surface tension is also attracted to carbon. Figure 3 is an example plot of initial foam height of Hitenol H-10 surfactant solutions as a function. NFPA categorizes foam concentrates into three expan-sion ranges as follows.
These proportioning rates make the use of Class A foam a cost effective means of combating fires because relatively small amounts of foam concentrate can be used to make effective foam. The pressure inside a foam of radius R that contributes to its self-destruction is 2γR. Surfactant transport from foam film to foam film is an essential yet poorly understood aspect of the viscoplastic yielding behaviour of flowing foam.
The energy need to increase the surface area A is γδAδt so a low γ means more foam for less energy. So a surfactant which reaches the lowest surface tension for the least amount of surfactant is in general going to give an easier longer-lasting foam. This smothering ability will act to isolate the fuel from other sides of the tetrahedron.
Surfactans will diffuse in water and absorb at interfaces between air and water or bet. Low ex-pansion foam has proven to be an effective means of controlling extinguishing and securing most flammable liquid Class B fires. 922 2021 A25 has however helped to advance understanding of the relevant surfactant transport processes.
In fact soap acts as a surfacatant and reduced the surface tension of water but at the same time it also causes air bubbles to become more stable. The word surfactant means surface active agent. Suppressing - Foams especially Class A are extremely effective at allowing.
LOW EXPANSION Expansion ratio up to 201. As a synthetic based foam concentrate Class A foam is applied at low concentrations ranging from 01 to 10. So a surfactant which reaches the lowest surface tension for the least amount of surfactant is in general going to give an easier longer-lasting foam.
Recent experimental and modelling work by Bussonnière Cantat J. It also gives water a foaming ability which allows water to remain and cling to vertical and horizontal surfaces without run off. At higher flow rates froth is encountered with both large fast bubbles and a population of smaller bubbles whose size decreases as the flow rate increases due to increased shear.
Class A foam is primarily a surfactant which is to say that it breaks down the surface tension of water. Class A foam will increase wetting effectiveness. It is trivially easy to make a foam - just mix air and liquid with some energy and bubbles will form.
Class A foam is deployed through a variety of portable and fixed appliance devices ranging. To investigate the foam stability during the foam formation each surfactant concentration was introduced with gas volumes of 25 and 50 cc during time period of 20 seconds. Class A Foam Increases Survivability for Civilians and Firefighters.
How a Foam Acts on a Fire Smothering - The use of a foam blanket will provide an excellent covering that can be used to surround a fuel thereby breaking a side of the tetrahedron. If these bubbles reach the surface with a liquid fraction ε in the 01-02 range then they are a kugelschaum kugel means sphere and schaum means foam. Due to its amphiphilic nature and unique feature of decreasing the interfacial tension the surfactant is widely used in every walk of life such as individual care products domestic cleaners.
As the name implies surfactants stir up activity on the surface you are cleaning to help trap dirt and remove it from the surface. Surfactants have a hydrophobic water-hating tail and a hydrophilic water-loving head. Because Class A foam acts as a surfactant when mixed with water its able to more effectively penetrate deep-seated fires including fires within mattresses sofas vehicle seats and other challenging items.
Emulsifiers are a class of surfactants which come in many different forms. By adding a small quantity of a Class A foam concentrate into a water stream the effectiveness of the water can be increased up to 5 times. The hydrophobic tail of each surfactant surrounds soils.
Cooling and wettin g are the primary extinguishing mechanisms. These fires are difficult to extinguish with water alone.

Despite Advantages Of Using Class A Foam To Battle Wildfires Use Is Down That Needs To Change International Fire Fighter

Ingredient Spotlight Surfactants

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
Foam Making Practical Surfactants Science Prof Steven Abbott

What Are Surfactants Surfactants Meaning Types Of Surfactants Surfactant Examples Anionic Surfactants
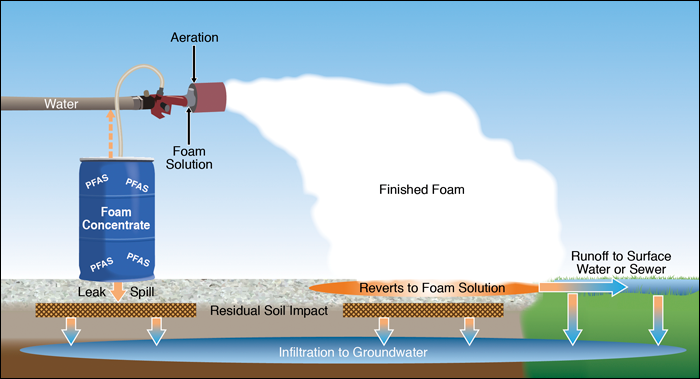
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
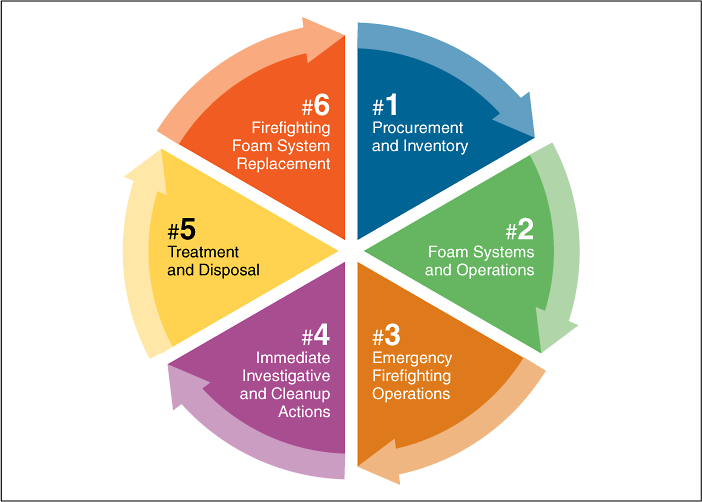
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
![]()
Class A Foam Is The Best Tool For Fighting Fires So Why Aren T Fire Departments Using It Claimsmate

Stability Of Foam An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Phos Chek Wd881 Class A Foam 5 Gallon Pail Linegear

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

Phos Chek Wd881 Class A Foam Fire Product Search

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

Types Of Firefighting Foam Vanguard Fire And Security

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
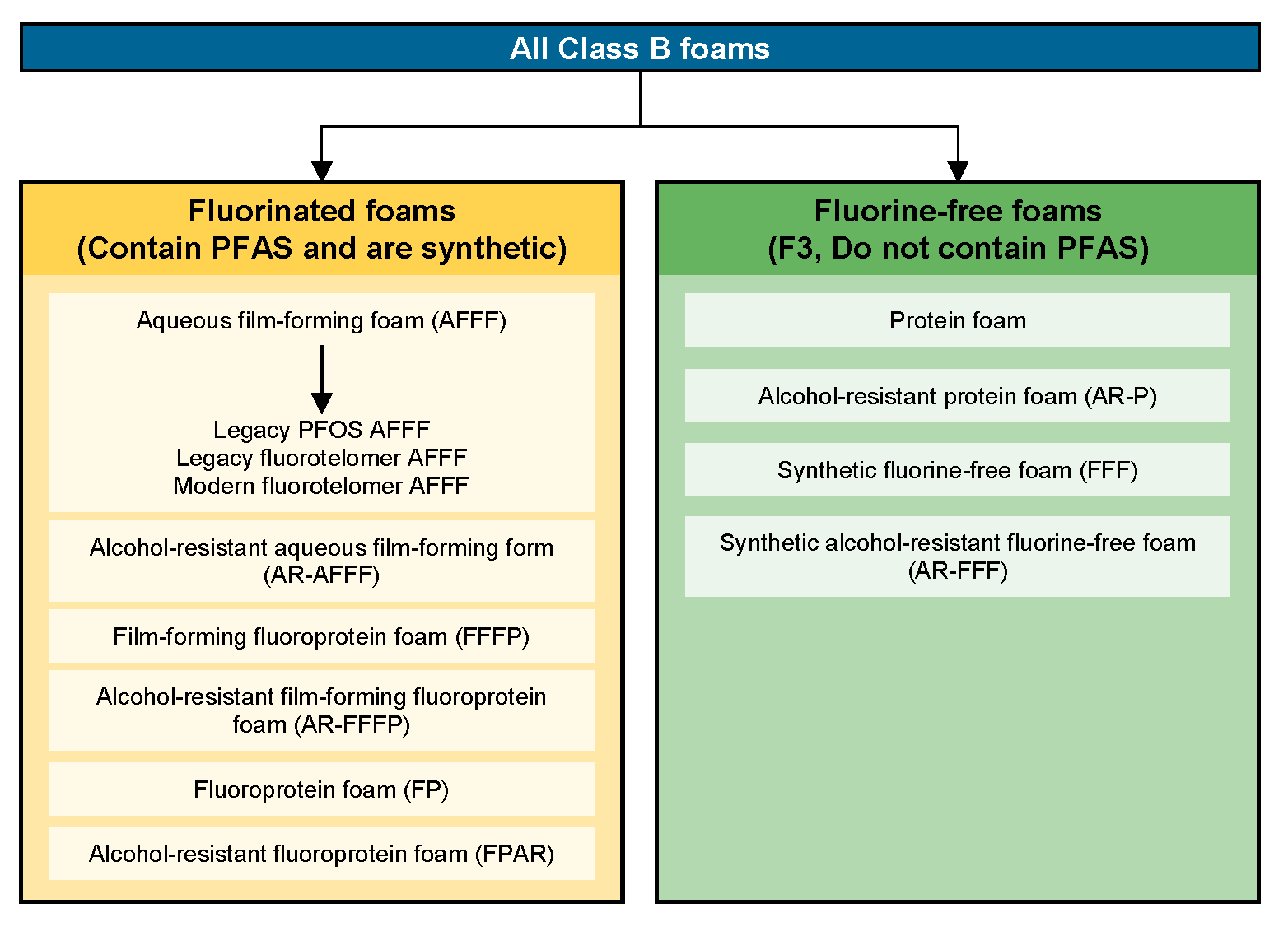
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
